Sindrome di Zellweger OMIM 214100
Sindrome di Zellweger OMIM 214100
redatto da P.Parisella
E' una rara displasia caratterizzata da anomalie cranio facciali, anomalie del SNC, anomalie scheletriche, epatomegalia.
E' trasmessa con carattere autosomico recessivo ed è dovuta a mutazioni dei geni PEX che causano difetti nella biogenesi dei perossisomi.
I segni ecografici che possono essere evidenziati in ecografia prenatale, anche se con difficoltà, sono:
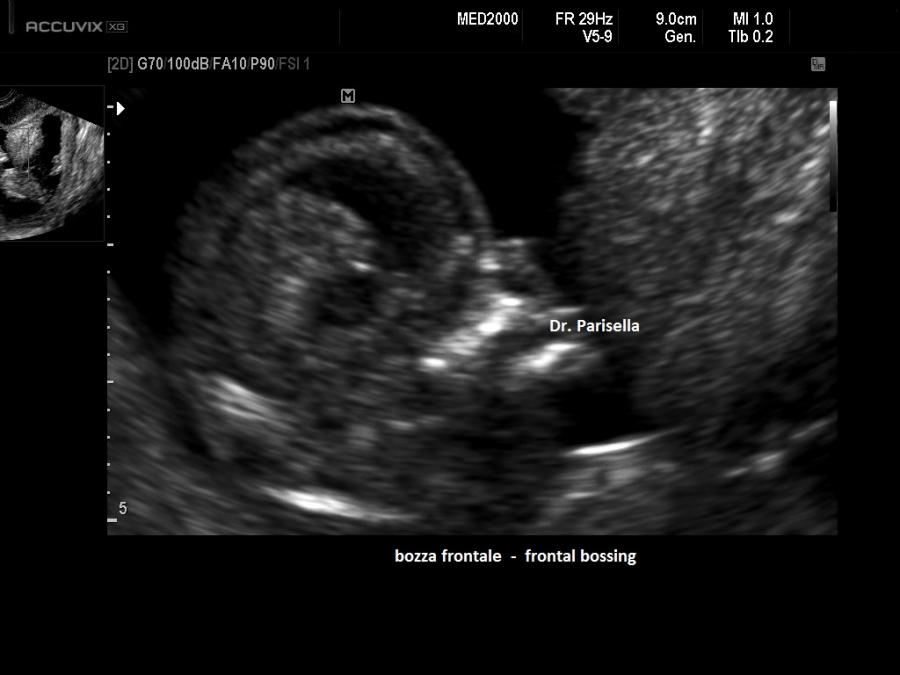
- dismorfismi cranio facciali: bozze frontali prominenti, radice del naso larga, facies appiattita
- anomalie scheletriche: condrodisplasia puntata (foci iperecogeni) interessante rotula e anca
- anomalie del SNC: agenesia del corpo calloso
- epatomegalia
Possono essere presenti ritardo di crescita, microcefalia, micrognazia, palato ogivale.
Bibliografia
Dancis, J.,
Hutzler, J. The significance of hyperpipecolatemia in Zellweger syndrome. Am.
J. Hum. Genet. 38: 707-711, 1986.
Ebberink,
M. S., Mooijer, P. A. W., Gootjes, J., Koster, J., Wanders, R. J. A., Waterham,
H. R. Genetic classification and mutational spectrum of more than 600 patients
with a Zellweger syndrome spectrum disorder. Hum. Mut. 32: 59-69, 2010.
Gilchrist,
K. W., Gilbert, E. F., Shahidi, N. T., Opitz, J. M. The evaluation of infants
with the Zellweger (cerebro-hepato-renal) syndrome. Clin. Genet. 7: 413-416,
1975.
Naritomi,
K., Hyakuna, N., Suzuki, Y., Orii, T., Hirayama, K. Zellweger syndrome and a
microdeletion of the proximal long arm of chromosome 7. Hum. Genet. 80:
201-202, 1988.
Naritomi,
K., Izumikawa, Y., Ohshiro, S., Yoshida, K., Shimozawa, N., Suzuki, Y., Orii,
T., Hirayama, K. Gene assignment of Zellweger syndrome to 7q11.23: report of
the second case associated with a pericentric inversion of chromosome 7. Hum.
Genet. 84: 79-80, 1989.
Opitz, J.
M., ZuRhein, G. M., Vitale, L., Shahidi, N. T., Howe, J. J., Chou, S. M.,
Shanklin, D. R., Sybers, H. D., Dood, A. R., Gerritsen, T. The Zellweger
syndrome (cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome). Birth Defects Orig. Art. Ser. V(2):
144-160, 1969.
Tamura, S.,
Okumoto, K., Toyama, R., Shimozawa, N., Tsukamoto, T., Suzuki, Y., Osumi, T.,
Kondo, N., Fujiki, Y. Human PEX1 cloned by functional complementation in a CHO
cell mutant is responsible for peroxisome-deficient Zellweger syndrome of
complementation group I. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 95: 4350-4355, 1998.
Volpe, J.
J., Adams, R. D. Cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome of Zellweger: an inherited
disorder of neuronal migration. Acta Neuropath. 20: 175-198, 1972.
Wanders, R.
J. A., Schrakamp, G., van den Bosch, H., Tager, J. M., Schutgens, R. B. H. A
prenatal test for the cerebro-hepato-renal (Zellweger) syndrome by
demonstration of the absence of catalase-containing particles (peroxisomes) in
cultured amniotic fluid cells. Europ. J. Pediat. 145: 136-138, 1986.
Wanders, R.
J. A., van Roermund, C. W. T., Schutgens, R. B. H., Barth, P. G., Heymans, H.
S. A., van den Bosch, H., Tager, J. M. The inborn errors of peroxisomal
beta-oxidation: a review. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 13: 4-36, 1990.
Wilson, G. N., Holmes, R. G., Custer, J.,
Lipkowitz, J. L., Stover, J., Datta, N., Hajra, A. Zellweger syndrome:
diagnostic assays, syndrome delineation, and potential therapy. Am. J. Med.
Genet. 24: 69-82, 1986